TRANSLATE THIS PAGE INTO ANY LANGUAGE
DO SUPERNOVA EFFECT
LIVING THINGS ON EARTH ?
SUPERNOVA, ETA CARINA,
AND YOU

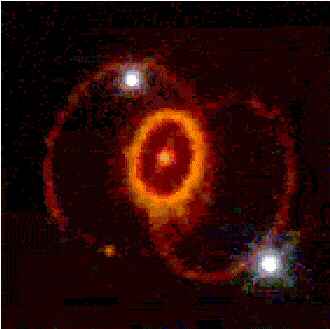
SUPERNOVA 1987A
We have talked much about Supernova 1987a.
The impending explosion is supposed to touch
the earth with its light.
But do Supernovas effect life on earth in any way.
Can we prove that they do..
The following is from the
Knight Tribune News Service.
I call your attention especially to paragraph 9
in the news release below.
Exploding Stars Supplied
Earths Atmosphere
Telescope reveals
'fountain of life'
Knight-Tribune News Service
ATLANTA
A new space telescope has revealed the inner workings of a
stellar factory that produces enormous quantities of oxygen.--
what one astronomer called "the real fountain of life.'
Scientists think most of the oxygen we breathe
was generated initially
by a relatively small number of
massive exploding stars known as "supernovae."
Along with other element.
The raw materials of 'new stars and planets
this precious gas eventually spread throughout the universe,
including our own solar system.
"Such massive stars create lots of oxygen
in their nuclear furnaces,
" Massachusetts Institute of Technology
astronomer

Claude Canizares
said yesterday
at the annual meeting of the
American Astronomical Society.
"It was explosions of such supernovae
that permitted life on Earth."
Once life evolved on this planet, oxygen generation
by bacteria and plants
became self-sustaining.
Thus, humans today are not dependent
upon supernovae for oxygen,
although such explosions continue to
spread it through the cosmos.
The ring-shaped remnants of one such supernova
labeled EO102-72 --
were studied on' two occasions last fall by
NASA's powerful
new Chandra X-ray Observatory "
When it blew up, the giant star,
15 to 25 times more massive than our sun,
was 200,000 light-years from Earth
in the Small Magellanic Cloud,
one of the galaxies closest to our own Milky Way.
(A light-year is about 6 trillion miles).
The brilliant light from the starburst reached Earth
about 1,000 years ago,
and could have been visible to the naked eyes of people
in Australia or South America, Canizares said.
Chandra, launched in July, carries an instrument called a
high-energy spectrometer that spreads out X-rays,
much as a prism breaks up a beam of light,
into a rainbow of different wavelengths.
It recognizes each element, such as carbon, oxygen, or iron,
by its unique wavelength.
The Chandra images showed that about half the gas expelled
by the exploding star was oxygen -- an unexpectedly high amount.
Elements such as iron and magnesium also were manufactured,
but in lesser amounts.
The oxygen from this supernova alone would
weigh as much as 10 of our suns,
and would be enough to supply 1,000 solar systems
like our own, Canizares said.
The gas formed inside the star,
where nuclear fusion of primordial
sulfur and iron.
"Understanding supernovae helps us to learn about the processes
that formed chemical elements like those which are found on Earth
and are necessary for life,"

said Kathy Flanagan,
another MIT astronomer.
"We have just seen a star rip its belly open
and show us what's inside."

Canizares said
after the oxygen was
"baked in the oven" he added,
it was "made available to those of us who like to take a breath."
The manufacture of oxygen and other elements
in stars continues to this day.
An enormous supernova exploded in 1987 and more are expected every
2 to 100 years.
THE ABOVE IS REFERRING TO
SUPERNOVA 1987A
WHICH I HAVE PROPOSED IS THE 7TH SEAL
OF THE BOOK OF REVELATION
However, a huge southern star called Eta Carina 9,000 light years away in
the Milky Way may have already blown up during the time it takes
its light to reach Earth, according to
Stephen Maran

an astronomer at
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
THE ABOVE IS REFERRING TO
ETA CARINA WHICH I HAVE PROPOSED IS THE 7TH ANGEL
OF THE BOOK OF REVELATION
IS THERE DNA
ACTUALLY COMING FROM ETA CARINA ?
This is from NOAO Astronomy Picture of the Day
In the text below, pay attention to the 3rd sentence
and the final sentence.
Astronomy Picture of the Day

Discover the cosmos!
Each day a different image or photograph
of our fascinating universe is featured,
along with a brief explanation written
by a professional astronomer.
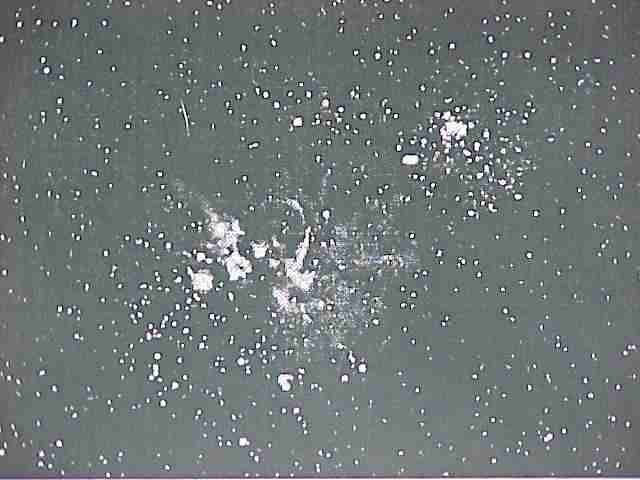
The Keyhole Nebula
Credit: NOAO;
Copyright: AURA, all rights reserved.
Explanation:
The dark dusty Keyhole Nebula, gets its name from its unusual shape.
Officially designated NGC 3324, the Keyhole Nebula is a smaller region
superposed on the larger Eta Carina Nebula.
These nebulae were created by the dying star Eta Carina,
which is prone to violent outbursts during its final centuries.
Noted and discussed as early as 1840 when a spectacular explosion
became visible, the Eta Carina system now appears to be
undergoing an unusual period of change.
An emission nebula that contains much dust, the Keyhole Nebula
is roughly 9,000 light years distant.
This photogenic nebula can be seen in the south
with even a small telescope.
The Keyhole Nebula was recently discovered to contain highly
structured clouds of molecular gas.
< Archive I Index I Search I Calendar I Glossary. I
Education I About APOD >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemlroff (MTU) & Jerr
http : / /www.sai.msu.su/ apod/ ap980112.html
What is important here is the last sentence of the text above.
The Keyhole Nebula was recently discovered to contain highly structured
clouds of molecular gas.
Molecular is DNA. (See Below).
The second thing to take note of is the
third sentence which says,
"These Nebulae were created by
the dying star Eta Carina.
Eta Carina created a nebula that contains
highly structured clouds of molecular gas.
Which means DNA created for a specific purpose.
DEFINITION OF MOLECULAR
mo-lec-u-lar (m...-luk"y...-1...r) adj.
1. Abbr. mol.
Of, relating to, or consisting of molecules.
2.
Of or relating to s'nnple or basic structure or form.
-mo,lec"u-lar"x-ty ('l2r"1-t n. --mo.lec"u.lar:ly adv.
Notice the definition of molecular as belonging to basic structures,
which would be DNA.
Let's go on with the definition
molecular biology n.
The branch of biology that deals,
with the formation, structure, and activity of macromolecules
essential to life, such as nucleic acids and proteins,
and especially with their role in cell replication and the transmission
of genetic information. --molecular biologist n.
MOLECULAR
TRANSMISSION OF GENETIC INFORMATION
NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA
So here we see molecular biology dealing with
macromolecules essential to life
such as nucleic acids and it specifically
says concerning their role
in cell replication and transmission
of genetic information.
And remember we were shown above that Eta Carina contains
highly structured molecular gas.
The definition referred to nucleic acids.
Lets look that up in the dictionary before we end here.
NUCLEIC ACIDS DEFINITION
nu-cle-ic acid (m-klÂ"% -kP"-, ny~-) n.
Any of a group of complex compounds
found in all living cells
and viruses, composed of
purine: pyrimidines, carbohydrates,
and phosphoric acid.
Nucleic acids in the form of DNA and RNA
control cellular function and heredity.
DNA and RNA to control heredity.
Coming from where.
AS YOU SAW WITH YOUR OWN EYES
So there is scientific proof that Supernova do effect the living things
on earth with life giving elements, and without them
life could not exist on this planet.
SO LET US KEEP OUR EYE ON SUPERNOVA 1987A !!
AND ETA CARINA
TO RETURN TO THE HIDDEN MEANINGS HOME PAGE